Posts
AI plays a crucial role in the development and operation of autonomous vehicles and intelligent transportation systems. Here are some key aspects of AI in this domain:
Read MoreAI Ethics is a critical and rapidly evolving field that focuses on the ethical considerations, guidelines, and principles surrounding the development, deployment, and use of artificial intelligence systems. Here are some key aspects of AI Ethics:
Read MoreAI has the potential to revolutionize education by providing personalized learning experiences, adaptive assessments, and intelligent tutoring. Here’s more information on these AI-based systems in education:
Read MoreAI has made significant advancements in the field of finance, revolutionizing various aspects of the industry. Here are some key applications of AI in finance:
Read MoreAI has significant applications in healthcare, revolutionizing various aspects of the industry. Here are some specific applications of AI in healthcare:
Read MoreRobotics is a field that combines Artificial Intelligence (AI) and engineering to design and develop intelligent machines capable of performing physical tasks autonomously. Here are some key aspects related to the integration of AI and robotics:
Read MoreExplainable AI (XAI) refers to the field of research and techniques focused on making artificial intelligence systems more transparent and interpretable. While AI algorithms can produce accurate predictions or decisions, they often operate as “black boxes,” making it challenging to understand how they arrive at their conclusions. This lack of interpretability can limit trust, accountability, and adoption of AI systems, particularly in critical domains such as healthcare, finance, and law.
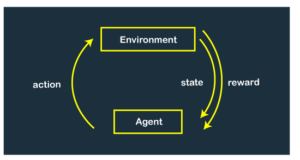
Read MoreReinforcement Learning (RL) is a subfield of Artificial Intelligence (AI) that focuses on developing intelligent agents capable of learning and making decisions by interacting with an environment. RL agents learn through a process of trial and error, where they receive feedback in the form of rewards or penalties based on their actions. Over time, they optimize their behavior to maximize the cumulative reward obtained from the environment. Here are some key aspects of reinforcement learning:
Read MoreComputer Vision is a branch of artificial intelligence that focuses on enabling computers to interpret and understand visual data, such as images and videos. It aims to replicate human visual perception and comprehension by leveraging machine learning algorithms and pattern recognition techniques. Here are some key aspects of Computer Vision:
Read MoreNatural Language Processing (NLP) is a branch of artificial intelligence (AI) that focuses on the interaction between computers and human language. NLP involves the development of algorithms and techniques to enable computers to understand, interpret, and generate human language in a way that is meaningful and useful. Here are some key aspects of NLP:
Read More